PERIODONTICS
What is periodontics?
Periodontics is a branch of dentistry that deals with diagnosing and treating periodontal gum diseases.
What are periodontal diseases?
Periodontal diseases include conditions which affect gums (gingiva) and destroy supporting tissues of the tooth (alveolar bone, cement, periodontal ligament), and can roughly be divided into: gingivitis (gingival inflammation) and periodontitis (periodontium inflammation).
Periodontal disease is a disease of today’s civilization. At the time when dental decay has almost disappeared in countries with well-organized dental health care, periodontal disease has become the main oral, as well as general health problem. Periodontal diseases are nowadays the leading cause of tooth loss in adults.
It is important to mention that periodontal diseases are progressive. Although their progression can be slowed down, it is difficult to completely stop it, and tissues that have been destroyed due to periodontal disease usually cannot be recovered.
What are the main causes of periodontal diseases?
The main causes of both periodontal disease and dental decay are bacteria found in dental plaque. Our mouth is inhabited by more than 350 species of bacteria, 20 of which are responsible for causing periodontal disease.
What is dentobacterial plaque?
Plaque is a soft, yellowish formation sticking to the surface of the tooth, especially at the gum line. It is formed only minutes after brushing. Inadequate hygiene, due to which food remains and dental plaque are not removed from the surface of the teeth, is the cause of the increasing number of these bacteria. Due to their presence, the immune response occurs, and in this mutual interaction of bacteria and defence mechanisms, inflammatory changes in the gum and periodontium are caused.
What is dental calculus and how is it formed?
Dental calculus is a hard mineralized deposit on the surface of the teeth. It is formed in about 7 days if dental plaque has not been removed from the surface of the teeth. Dental plaque is acid, and the organism is trying to neutralize the acidity by depositing minerals from the saliva into the plaque. Plaque gradually becomes calcified and turns into calculus.
There are supragingival (above the gum line) and subgingival (below the gum line) calculus deposits.
Calculus represents a secondary etiological factor in the development of periodontal disease. It does not cause inflammation, but due to its porosity and roughness it functions as a large bacterial niche, which makes its professional removal extremely important in the prevention of periodontal disease.
What are the symptoms indicating periodontal disease?
The indicating symptoms which, if left untreated, lead to deterioration of the surrounding bone and tooth loss include: swollen, red gums, bleeding, bad breath, slightly loose teeth.
Patients with severe gum disease and loose teeth are usually not aware of the fact that those teeth are lost and cannot be saved in any way. Reconstructing those teeth, gums and bone is very complex and demanding.
Is everyone equally susceptible to periodontal disease?
Not everyone is equally susceptible to periodontal disease. Apart from the genetic predisposition, there are certain risk factors for the development of periodontal disease.
Gingivitis may also occur during pregnancy, puberty, due to hormonal changes or consumption of certain drugs (phenytoin, cyclosporine, nifedipine).
Periodontal disease may affect all age groups: it occurs in about 35% of people over the age of 30, but can also occur in children. 63% of adult patients suffer from mild form of gum disease, while 37% suffer from moderate or advanced periodontitis. In patients who are over the age of 40, periodontal disease is the leading cause of tooth loss.
What are the risk factors for the development of periodontal disease?
The main risk factor for the development of periodontal disease is smoking. Different components of tobacco smoke have harmful effects primarily on oral mucosa. It is important to mention that nicotine, among other things, causes constriction of small blood vessels, which makes it difficult to notice first symptoms of periodontal disease. Since there is no bleeding during tooth brushing, the disease progresses without any external symptoms, while in deeper tissues the loss of bone can be noticed, so smokers turn to dentists for help after the disease has severely progressed and caused their teeth to become loose or fall out. Apart from being a risk factor for periodontal disease, smoking also causes oral cancer and has a negative effect on periodontal wound healing, which gives another reason to encourage smokers to quit smoking. Besides smoking, another risk factor for development of periodontal disease is diabetes. It is a well-known fact that patients with diabetes, especially if it is not controlled, are more susceptible to periodontal destruction.
Another group of risk factors, which are also called risk indicators includes: osteopenia, osteoporosis, stress, nutrition (lack of calcium, vitamin C, proteins), medications and genetic factors. This group also includes immune system diseases, such as AIDS. It is clear that people with one or more risk factors and/or indicators should conduct excellent oral hygiene. In order to maintain both oral and overall health it is important to avoid smoking and drugs, be physically active, exercise, have a good night’s sleep and healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C and calcium.
Why does periodontal disease pose a threat to the overall health?
A large number of microorganisms present in the mouth of the patient suffering from periodontal disease is very harmful to the overall health. For some time already, periodontal disease has been considered a risk for development of certain systemic diseases. Periodontitis can increase the risk for development of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, diabetes, respiratory diseases and preterm birth and low birth-weight.
Patients suffering from periodontitis most usually develop cardiovascular diseases. There is data linking periodontitis with an increased risk for atherosclerosis and thromboembolic events. Patients with periodontitis are twice as likely to develop coronary heart diseases and have a three times higher risk of a stroke.
Periodontitis is a risk factor for respiratory diseases as well. Bacteria from the dental plaque can be aspirated into the lower respiratory tract causing lung infection, especially in older and seriously ill patients.
The research has shown that there is a link between periodontal disease and preterm birth. Actually, pregnant women with periodontal disease have a 7 times higher risk of preterm birth, and in some cases it can lead to intrauterine growth restriction. The most probable reason for that is a labour-inducing compound (prostaglandin) which can be found in oral bacteria. High levels of prostaglandin are found in women with severe cases of periodontal disease.
Research has recently shown that in patients with diabetes periodontitis can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels, thus increasing the risk of diabetes complications. Controlling periodontitis can help those patients control their diabetes.
The latest research shows that inadequate oral hygiene also increases the risk of: dementia, erectile dysfunction and impotence in men under the age of 30 and over the age of 70. Periodontal diseases are more common in people with rheumatoid diseases. The research has shown that people who do not maintain oral hygiene have higher levels of inflammation-related proteins, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and fibrinogen.
How to prevent periodontal disease?
Due to the fact that periodontal disease is primarily the consequence of inadequate dental and oral hygiene, the most important thing to help fight it is regular and proper oral hygiene. It is the most accessible, efficient and cheapest way to achieve oral health. Therefore, patients themselves can prevent the development of periodontal disease by proper hygiene.
In order to maintain health of Your teeth and gums, brush Your teeth after each meal, 2-3 times a day, especially in the evenings. Using dental floss and/or interdental brushes is necessary to remove the plaque and food remains between the teeth. Most toothpastes contain flour and antibacterial substances which, apart from fighting tooth decay, also attack bacteria responsible for periodontal disease. It is recommended to replace your toothbrush with a new one every 1-3 months. Nowadays soft brushes with a large number of synthetic fibres of the same length are advisable. The choice of toothpaste is not as important as the use of proper brushing technique (10 short tips on how to properly brush your teeth). Toothpaste should be squeezed onto a dry toothbrush and taken to mouth dry since there is enough liquid in the mouth to make the toothpaste foam, without softening the bristles before brushing. Teeth and gums should be brushed using circular motions, holding your brush at a 45-degree angle in relation to the tooth surface. While brushing, make sure that bristles reach the space between Your teeth and gums (as far as the gum line allows- do not force it). Brush each quadrant separately, and all visible surfaces of the teeth: biting surface, cheek surface and tongue surface. Surfaces between the teeth that touch each other should be cleaned additionally by using dental floss and/or interdental brushes. Periodontists recommend interdental brushes. They are an ideal instrument for cleaning spaces under prosthetic devices, around dental implants and in the case of deep periodontal pockets. Disinfectant liquids for mouth rinsing (based on chlorhexidine) can be used as an oral hygiene supplement only when recommended by a dentist.
It is important to brush your teeth properly because improper technique of tooth brushing will fail to prevent the development of periodontal disease and can also lead to further deterioration of hard and soft oral tissues.
In order to maintain both oral and overall health it is important to avoid smoking and drugs, be physically active, exercise, have a good night’s sleep and healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C and calcium.
Apart from adequate oral hygiene, prevention of periodontal diseases also includes regular dental visits and professional teeth cleaning. Regular dental visits every 6 months allow us to notice oral problems at an early stage, they facilitate treatment and prevent greater deterioration. Regular dental check-ups are also extremely important for patients diagnosed with periodontal disease since the disease is activated cyclically and without good patient-doctor communication, there are no long-term results.
DENTAL CALCULUS REMOVAL
Why is it important to have calculus removed regularly?
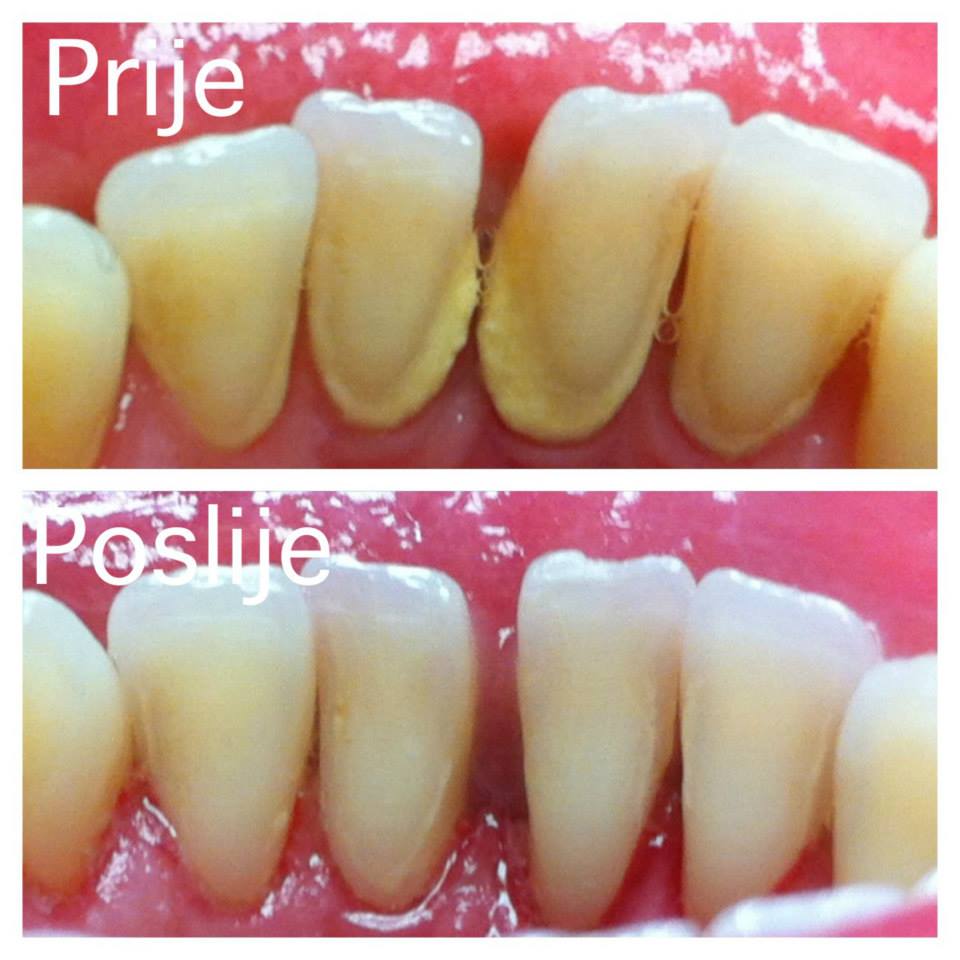
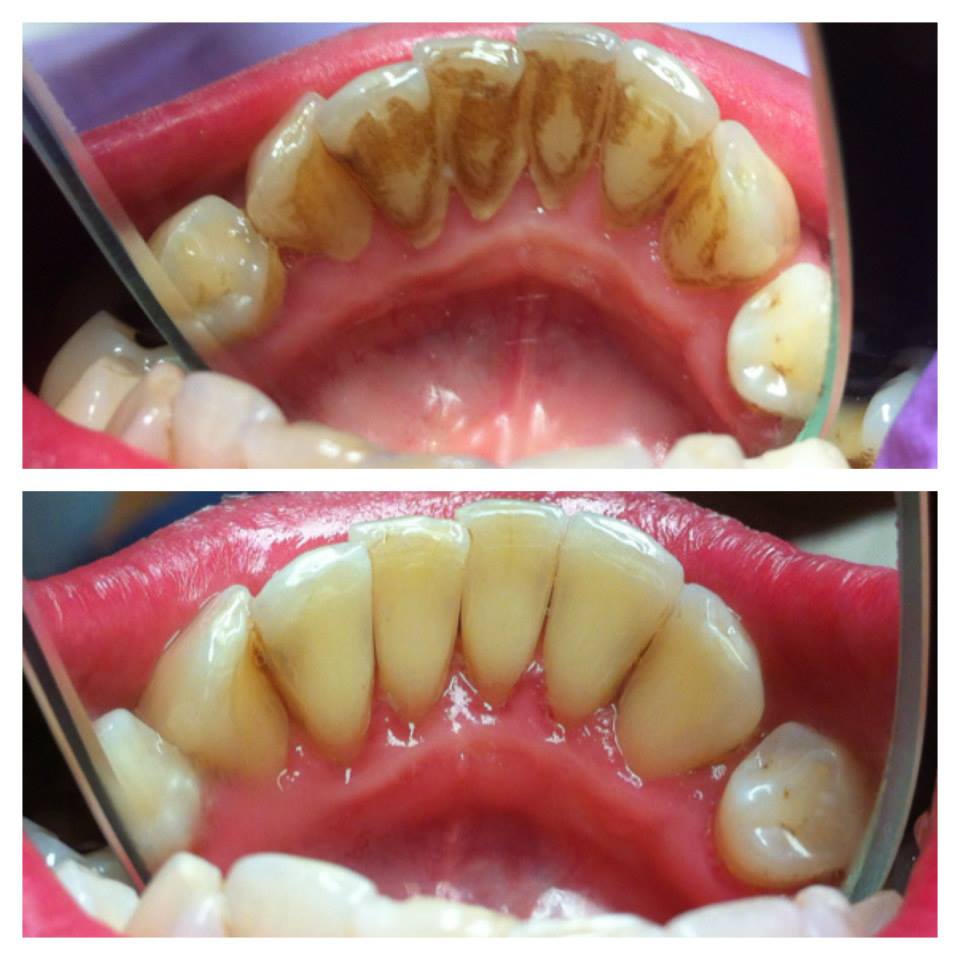
Removing dental calculus every 3-6 months helps maintain oral health. Apart from soothing gum inflammation and bleeding, removing dental calculus also helps eliminate bad breath and tooth pigmentations which form due to smoking, drinking coffee and tea. Following the calculus removal, the teeth are polished to make Your smile brighter and nicer.
How is calculus removed?
Dental calculus is removed in the dental office most usually by using ultrasonic instruments which ensure painless calculus removal without damaging the tooth surface with plaque and calculus deposits.
- After the initial oral examination to determine the presence of the dental calculus, all tooth surfaces containing plaque, discolorations and calculus are cleaned.
- The next step includes interdental calculus cleaning using interdental polishing strips, and polishing all tooth surfaces using polishing brushes and a polishing paste.
How long does it take to have the calculus removed?
Dental calculus can usually be removed in just one treatment which lasts 30-45 minutes, depending on the amount of calculus deposits.
DENTAL SANDBLASTING
What is dental sandblasting?
Dental sandblasting is a completely painless method of professional cleaning of deposits on the tooth surface (plaque, pigmentation, cariogenic bacteria) by high-pressure jet of water and powder.
What does sandblasting powder consist of?
The sandblasting powder consists of small particles of sodium bicarbonate available in several different flavours, such as menthol or fruit flavour which make the procedure more pleasant for the patient. The powder particles are round in shape, with no sharp angles, the size of 60-70 microns. It is precisely such a geometric shape that allows the creation of large kinetic energy of particles which, in contact with the tooth, makes a large contact surface. These small microabrasive particles which are scattered in the water are propelled under high pressure by a sandblasting machine, successfully removing deposits and pigmentations from teeth surfaces, restoring their natural colour and shine.
What is achieved by dental sandblasting?
By dental sandblasting fast and efficient removal of unaesthetic yellow and dark stains and soft deposits from teeth surfaces can be achieved. Stains form due to frequent consumption of cigarettes, coffee, tea and other coloured drinks. Following the procedure, teeth are shiny and polished and less susceptible to plaque deposits and pigmentations.
What is the procedure for sandblasting?
Sandblasting is performed in one visit. If possible, it should be performed after removing dental calculus to achieve the best possible result. The procedure lasts 15-30 minutes, depending on the amount of deposits. It is non-invasive, safe and completely painless.
Sandblasting is recommended before teeth whitening so that the whitening agent can efficiently whiten the whole surface of the tooth.
What to do after sandblasting?
After the treatment, it is not allowed to smoke, eat or drink coloured, fizzy and pigmented drinks and foods for 2-3 hours. One hour after the treatment, it is allowed to drink uncoloured drinks, water.
What to do in the case of progressed periodontal disease?
If the periodontal disease has progressed and there are signs of slightly loose teeth, subgingival calculus deposits, bone pockets and receding gums, it will be necessary, along with dental cleaning, to perform curettage (the mechanical removal of deposits from root surfaces). Additionally, antibiotic therapy should be applied. Slightly loose teeth can be fixed by joining the teeth together (teeth splinting with everStickPERIO). In the case of extensive alveolar bone loss, it is necessary to apply other periodontal surgical procedures. Treating periodontal diseases timely is of extreme importance. By doing so, the disease progression can be slowed down, or even stopped, while recovering damaged tissues is almost impossible. Reconstructing lost tissues requires complex and expensive surgical-prosthetic therapy.
Why choose to undergo periodontal treatments in OUR practice?
- We have years of experience in treating periodontal diseases.
- We try to make you feel comfortable and relaxed in our practice, without any fear.
- We respect your wishes relating to the health and beauty of your future smile and try to fulfil them completely.
- Our goal is to make your smile functional and aesthetically perfect.
- The work in your mouth will be painless and safe, we will do our best to make it as comfortable as possible and our service as good.
- Your “before and after“ photos of periodontal treatment will be preserved.
- At any moment we are available to you for advice and consultation via mobile phone, e-mail and social media.
- We try to keep our appointments.
- You can pay in cash, but also in interest free instalments: American Express up to 12 instalments, Diners up to 6 instalments, Erste & Steiermärkische bank Maestro and MasterCard up to 12 instalments.
- There is free parking in front of the practice.
If we meet your criteria, feel free to contact us and make an appointment.
If these pages do not provide you with an answer to your question on periodontal diseases, dental health and dental services, feel free to contact us.
We are at your disposal!
| Radno vrijeme
PON, SRI, PET 9:00-16:00
UTO, ČET 13:30-20:30
☎ +385(0)1 4822 137